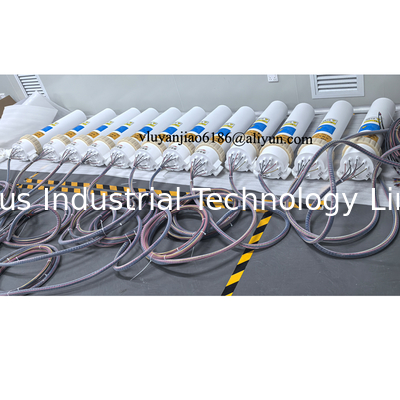
Designed for durability, performance and safety while heating chemicals/acids or ultrapure DI Water.
PTFE surfaces for permeation protection.
Suitable for single pass, recirculating and steam applications.
The inline chemical heater offers unmatched performance and reliability with the ability to heat a variety of chemicals and ultrapure DI water.
This heater is suitable for either single pass or recirculating applications.
Delivers best-in-class performance over a wide range of flow and temperature requirements.
The inline chemical heater is the most durable and long-lasting inline heater available!
Multiple plumbing layouts facilitate easy installation into a variety of tool configurations.
Fluoropolymer (PTFE) surfaces protect from permeation.
Notes
1) This product must be installed vertically
2) The use process must be grounded
3) Water must be passed before heating
4) Product size and technical parameters can be customized according to customer needs
Applications
Semiconductor Wet Processes
Sterilization/Cleaning
Solar/Photovoltaic Wafer Cleaning
Industries
- Semiconductor Fabrication
- Solar Cell Manufacturing
- Flat-Panel Display, LEDs & Electronics
- Chemicals Manufacturing
- Industrial Manufacturing
-
An inline chemical heater is a device that heats a fluid as it flows through a pipe or tube, rather than heating a whole tank of liquid. These heaters are designed to quickly heat the fluid at the point of use, offering advantages like faster heating, reduced heat loss, and improved efficiency. They are commonly used in industrial settings for heating chemicals, solvents, and other fluids in processes like semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and fluid handling.
Key Features and Benefits of Inline Chemical Heaters:
Fast Heat-up:
Inline heaters allow for rapid heating of continuous fluid flows, eliminating the need to wait for an entire tank to reach the desired temperature before using the heated fluid.
Point-of-Use Heating:
The fluid is heated directly where it's needed, minimizing heat loss and energy consumption.
Efficient Energy Usage:
Focusing heat on the flowing fluid reduces energy waste compared to heating a large volume.
Versatile Applications:
Inline heaters are available in various designs and materials to handle a wide range of chemicals, solvents, and temperatures.
Material Compatibility:
Many inline heaters are made with materials like stainless steel, fluoropolymers (PFA/PTFE), quartz, and titanium to resist corrosion and chemical reactions.
Safety Features:
Some inline heaters incorporate features like gas purging to remove chemical permeation, temperature sensors, and self-limiting technology for safe operation in various conditions.
Customization:
Options for single-pass or recirculating applications, different power outputs, and various fluid connections enable customization for specific process needs.
Low Wattage Options:
Some inline heaters are designed for low wattage, making them suitable for sensitive chemistries and applications where maintaining precise temperature control is crucial.
Applications of Inline Chemical Heaters:
Semiconductor Manufacturing:
Heating chemicals for cleaning wafers, stripping resist, and various process steps.
Chemical Processing:
Heating and maintaining temperatures for chemical reactions, mixing, and other process steps.
Solvent Handling:
Heating solvents for use in cleaning, extraction, and other applications.
Ultra-High Purity (UHP) Applications:
Inline heaters designed for ultra-high purity materials are essential for processes like deionized water heating, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and advanced materials science.
The Parts Of An Inline Heater
Inline heaters are made up of a number of different parts:
The heating element and its sheath and thermal insulation.
The pump unit that pushes the fluid to be heated through the system.
The fluid itself, which passes through a loop around the heating element, getting hotter with each pass.
The outlet nozzle where the heated fluid is pushed out of the system once it reaches the correct heat.
Thermocouple sensors that determine when the liquid has reached the desired temperature.
A control system that varies in its complexities – some allow the unit to be turned on and off, but have a set temperature, while others are more flexible and allow the user to change the temperature.
There are some optional components that can be added to an inline heater. These include stronger cases that are moisture resistant or are strong enough to contain an explosion. Additional flange types and mounting equipment are also available.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 



